Inserting Media into Posts and Pages
Languages: English • 日本語 (Add your language)
Contents
Overview
When creating or editing a WordPress page or post, you can easily embed many different types of media at any time using the WordPress Add Media tool.
Embeddable media include:
- Images
- Audio
- Video
- Documents of various types
The following will take you step by step through the process of embedding media into your content.
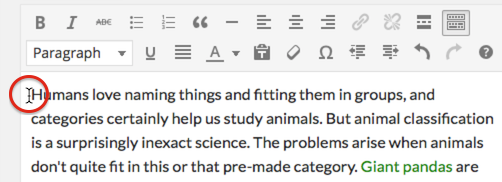
Step 1 – Placing your cursor
In order to embed media in your page or post content, you must first insert your cursor in the place in the text where you want the media to appear. By placing your cursor within your text, you can embed media inline with your content. You can also place your cursor on a blank line if you want the media to appear by itself.
Tip: It’s a good idea to place your cursor on the left margin of your text, even if you want media to appear on the right. This is because there is a special setting called Alignment that allows you to control whether the image appears on the right or the left side of the text. It even automatically controls how text flows around media embeds.
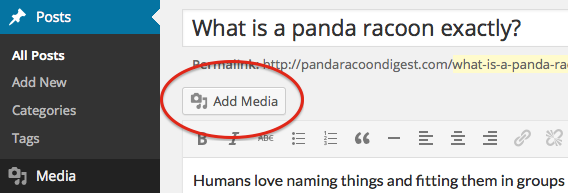
Step 2 – Click the Add Media button
Once you’ve placed your cursor on the line where you want your media to appear, click on the Add Media button to launch the media uploader interface, then select the Insert Media option from the list of actions in the left side of the media uploader window.
As of WordPress Version 3.9, you may also drag media directly onto the editor to upload them.
Step 3 – Add or Select Your Media
You can upload or select the media you want to add to your page or post by choosing from either of the following options in the center of the media uploader window:
- Upload Files: Upload the media you want to use from your computer by dragging it into the upload area.
- Media Library: Select from any previously uploaded media in the media library by clicking on the one you wish to add to your page or post.
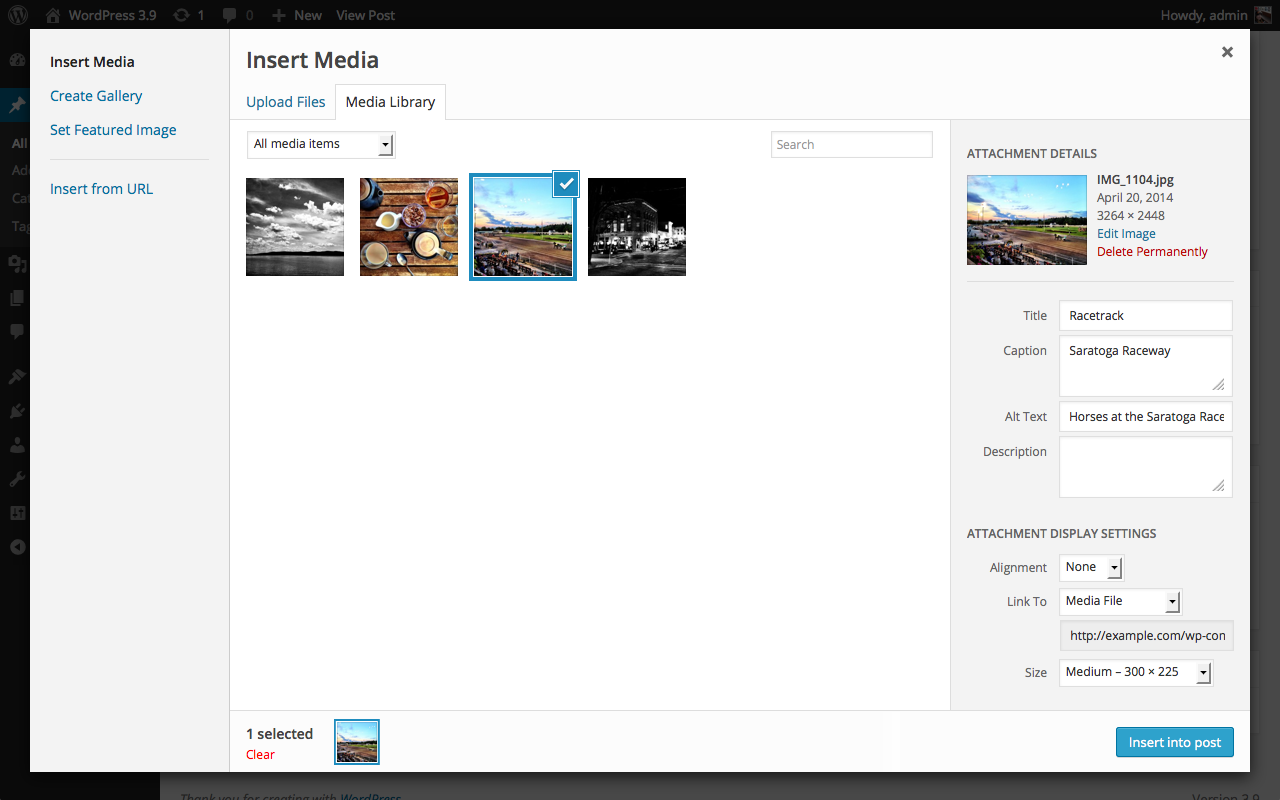
Once you have selected or uploaded the media you want to add, you will see a checkbox next to the thumbnail confirming your selection, and you will see the selected media displayed in the Attachment Details pane on the right hand side of the media uploader interface.
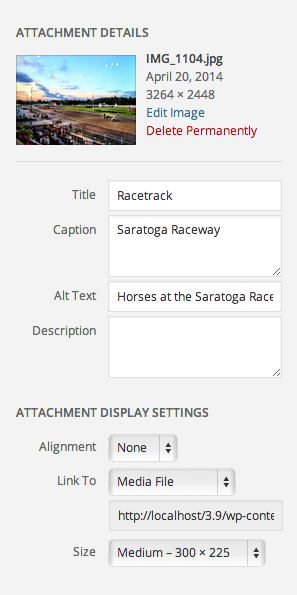
Step 4 – Attachment Details
The Attachment Details pane displays a small preview or icon as well as important information such as the filename, date uploaded, and dimensions in pixels for image files or length for audio/video files.- Title
- The name of this media.
- Caption
- Brief explanation. This text will be displayed below the image.
- Alternate Text
- This text is required with all images for improved accessibility for those with impaired or low vision who may be using screen readers or other assistive technologies. Use text that makes sense when read out loud along with the context of any text that appears before or after the image on the published page. If the textual context is already present, there is no need to duplicate the text. Instead, use the alt text to add information or an additional detail or two about what is actually in the image.
- Description
- An explanation of this particular media.
The Attachment Display Settings pane controls how the media embed will be displayed when viewed on the site. - Alignment
- Left, Center, Right, or None
- Link To
- Media File, Attachment Page, Custom URL, None
- Link URL
- Read-only display of the media URL or web address.
- Size
- Thumbnail, Medium, Large, Full Size
Available sizes depend on what sizes were generated for the image at the time it was uploaded based on the sizes in Settings > Media compared to the original image size. The new image will only be generated if it the dimensions are equal to or smaller than the original image size.
For images, there are also action links that allow you to Edit Image, which takes you to the Edit Media page, or to Delete Permanently to remove the image from your site.
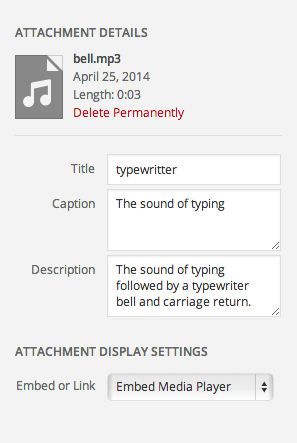
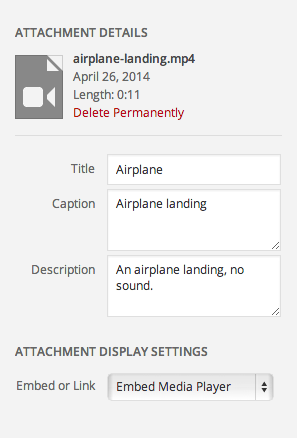
Audio and video files have embed options instead of alignment, link, and size options.
Embed or Link:- Embed Media Player
- Link to Media File
- Link to Attachment Page
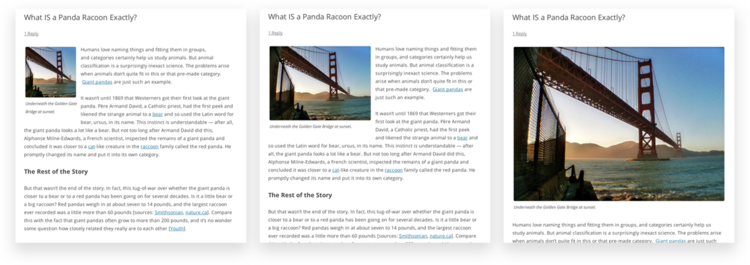
Image Alignment
The Alignment setting allows you to determine where you would like the image to appear in your content area and how it interacts with any text on the page. You have the following image alignment options to choose from:
- Left: Aligns the image on the left-hand margin, and any text that is on the page wraps (or flows) around the image to the available space on the right.
- Right: Aligns the image on the right-hand margin, and any text that is on the page wraps (or flows) around the image to the available space on the left.
- Center: Aligns the image to the center of the page, with no text displayed around it.
- None: Inserts the image into the page with no alignment
| Top row: Left and Right alignments. Bottom row: Center and "None" alignments |
Image Link
The Link To settings determines where someone is taken when they click the image. You can specify the following image link settings:
- Attachment Page: Links your inserted image to its WordPress media attachment page.
- Media File: Links your inserted image directly to the original, full-size version of the file.
- Custom URL: Allows you to set a custom link URL for your inserted image to link to when clicked.
- None: This setting will remove the link completely, rendering the image “un-clickable”.
Image Size
The Size settings determine the size of the image you are adding to your site. By default WordPress creates a range of four image size for you to choose from:
- Thumbnail: Displays a small thumbnail-sized version of your image on the page/post. Note, by default the Thumbnail size is a square, so some cropping of your original image may occur.
- Medium: Displays a medium-sized version of your image on the page/post. This is a good size to use with Left/Right alignments, as it leaves sufficient space for legible text to either side.
- Large: Displays a large-sized version of your image on the page/post. Note: WordPress will determine the width of the content column of your theme, and display the largest possible image for that space.
- Full Size: Displays a full-sized version of your image on the page/post. Note: WordPress will determine the width of the content column of your theme, and display the largest possible image for that space. If your original image is larger than this column width, the full size of the image may not be displayed.
| Thumbnail, Medium, and Large image sizes (Image Alignment: Left) |
You can visit the Settings > Media section of your WordPress dashboard to customize the image sizes. Note that the sizes and the thumbnail crop are set at the time the image is uploaded. Those generated images then become the size options shown here.
As of WordPress Version 3.9, you can now grab the handles that appear when you click on an image and resize the image by dragging.
Step 5 – Inserting Media
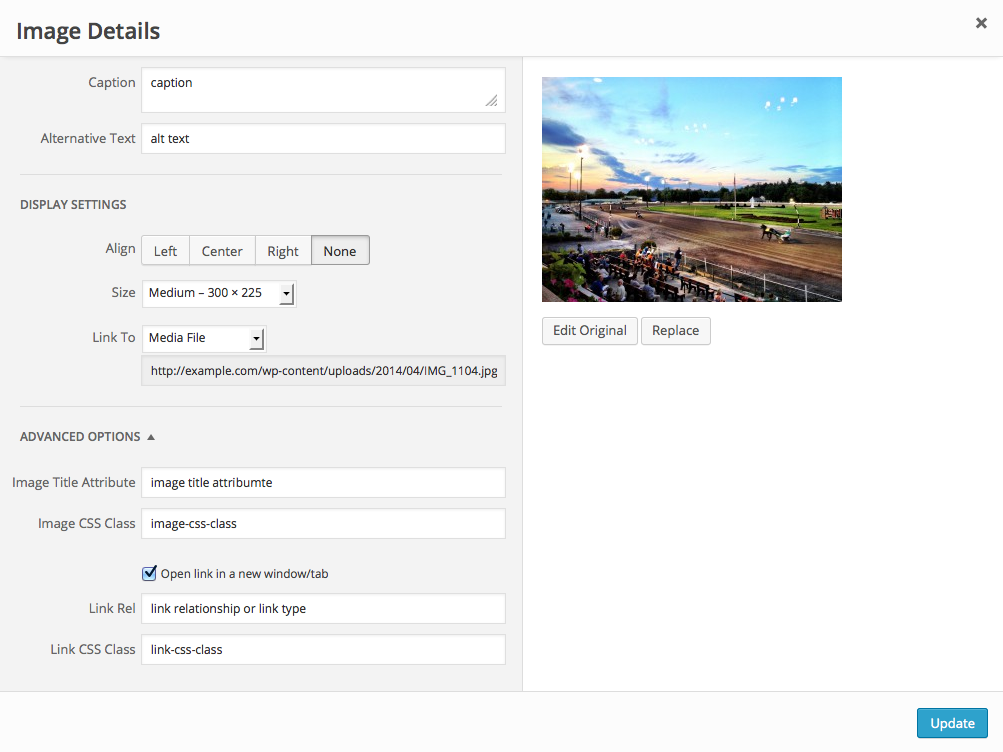
Once you have determined your embed settings, click on the Insert into post or Insert into page button at the bottom right to add the media. After the media uploader window closes, you will see the media in the editor window.Image Details
There are several options available for modifying image details after an image has been added. To change image details, click on an image in the editor and then click the edit icon to open the Image Details screen, or remove the image by clicking the "x" icon. You can adjust the alignment of the image by clicking Align left, Align center, Align right or No alignment icons.
The Image Details screen can be used to modify image attributes for individually inserted media files. Click the "Advanced Options" heading to see additional options.
- Caption: Brief explanation. This text will be displayed below the image.
- Alternative Text: Text to described the media. Used by screen readers.
- Align: Image placement within the content area.
- Size: Selected sizes based on images sizes generated at upload time.
- Link To: Destination when someone clicks on an image.
- Image Title Attribute: Sets a title for the "img" HTML tag. Used as a tooltip that appears when you hover over the image.
- Image CSS Class: Adds a CSS class to the "img" HTML tag that can then be used to style the image via a custom CSS plugin or a child theme.
- Open link in a new window/tab: Adds
target="_blank"to the link HTML. - Link Rel: Sets the link relationship or link type.
- Link CSS Class: Adds a CSS class to the link HTML that can then be used to style the link via a custom CSS plugin or a child theme.
Here is the output by the Image Details shown in the example above:
[caption id="attachment_16" align="alignnone" width="300"]<a class="link-css-class" href="http://example.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/IMG_1104.jpg" target="_blank" rel="link relationship or link type"><img class="image-css-class wp-image-16 size-medium" title="image title attribute" src="http://example.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/IMG_1104-300x225.jpg" alt="alt text" width="300" height="225" /></a> caption[/caption]
Changes in 3.9
As of WordPress Version 3.9, some image details settings such as borders, margins, and styles are no longer available in the Image Details screen to try to encourage best practices in content management by reducing the amount of inline styling added on a per-image basis. Adding inline styles instead of relying on the theme or custom CSS can lead to bloated HTML which can then make it difficult to keep images looking good in various display sizes (including mobile views) or after switching themes. Ideally, a well-coded theme will handle image borders and margins sufficiently. However, if you do still want to add inline styles for some images manually, you may still do so using HTML editor by clicking the Text tab at the top right of the edit area and adding inline CSS. There are also plugins available, such as Advanced Image Styles, which will add back options in the Image Details screen for image borders and margins.
The source field was changed to a "Replace" button located just below the image inside the Image Details screen. If you want to use an image that is not located in your media library and that you don't want to upload into your media library, you should add it by using the Add Media > Insert from URL option.
Resources
- Using Image and File Attachments
- Embeds - Inserting different medias.
- Photoblogs and Galleries - Using WordPress as photoalbum, photoblog etc